
- PRONE POSITION DEFINITION PROFESSIONAL
- PRONE POSITION DEFINITION SERIES
- PRONE POSITION DEFINITION FREE
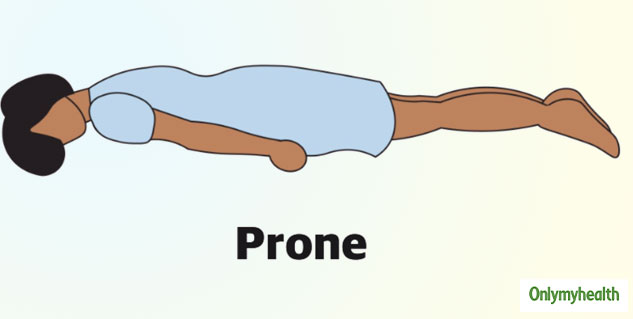
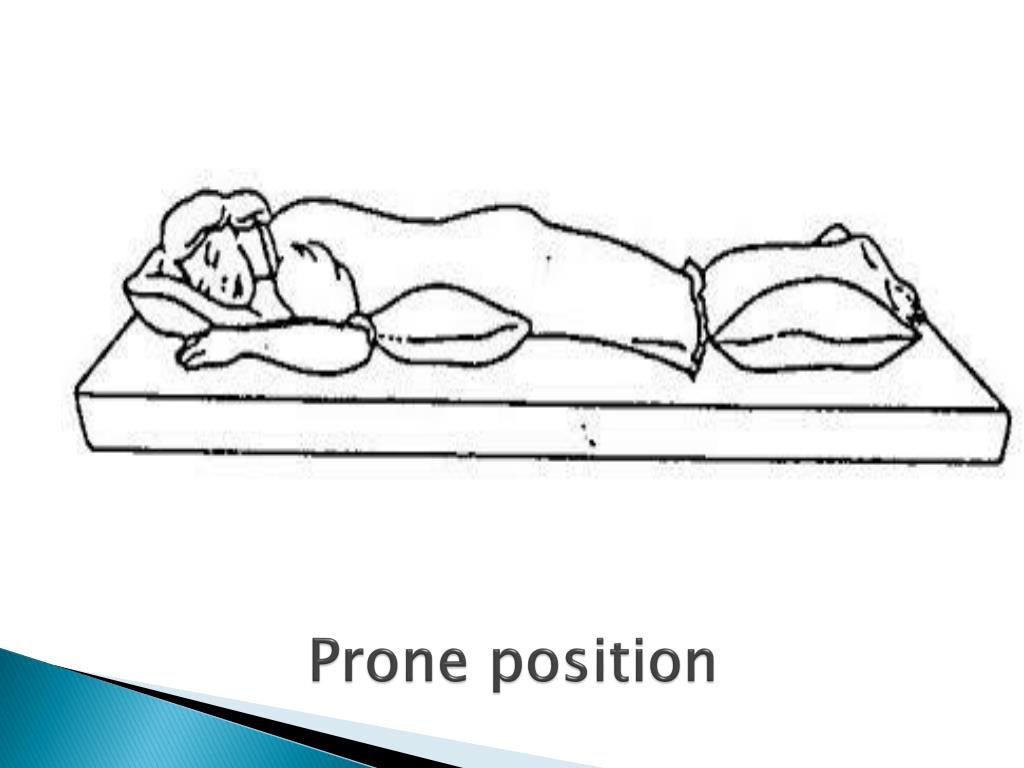
Damage to the brachial plexus and ulnar nerves if not protected.Potential for decreased functional residual capacity (FRC) 3.The patient’s arms are in a neutral thumb-up or supinated position may be tucked at their sides or abducted to less than 90 degrees on armboards. The patient is face-up, with their head resting on a pad positioner or pillow and their neck in a neutral position. The patient’s head is in a neutral position without excessive flexion, extension, or rotation. The arms may also be tucked at the patient’s side. The arms are abducted less than 90 degrees with the elbows flexed and palms down to maintain neutral alignment of the arms and wrists. The patient’s arms are extended and secured on armboards at a lower level than the chest. This leads to an improvement in the ventilation/perfusion matching and consequently, an improvement in oxygenation. The prone position produces an increase in functional residual capacity and alterations in the distribution of both ventilation and perfusion throughout the lungs. The prone position offers surgical access to the dorsal (posterior) aspects of the patient’s body, such as the spine, neck, and shoulders. At a minimum, four people should be available when turning a patient prone and both the cart and Operating Room table should be locked.Ĭomplications associated with prone position include: 1,2 Pressure should be kept off of the patient’s eyes, cheeks, and ears. The patient’s face should be monitored when in the prone position. Ensure a gurney is always readily accessible to reposition the patient from the prone position to the supine position if cardiopulmonary resuscitation becomes necessaryĪs with all surgical positions, surgical staff should be aware of risks to the patient in the prone position.Prevent direct pressure on the patient’s eyes.Use a face positioner when the patient’s head is in midline.Elevate the patient’s toes off the bed with padding under the shins.
PRONE POSITION DEFINITION FREE
Ensure the breast, abdomen, and genitals are free from pressure.Use chest supports that extend from the clavicle to the iliac crest.When positioning a patient in prone, surgical staff should use safe practices and guidelines: The prone position is often used for spine and neck surgeries, neurosurgery, colorectal surgeries, vascular surgeries, and tendon repairs. 1,2 When Would You Put a Patient in the Prone Position? Some common procedures that are performed while the patient is in the prone position include spine and neck surgeries, neurosurgeries, colorectal surgeries, vascular surgeries, and tendon repairs. The patient’s arms should be abducted less than 90 degrees with the elbows flexed and palms down to maintain neutral alignment of the arms and wrists. 1 In the prone position, the patient is positioned face-down with their head in a neutral position without excessive flexion, extension, or rotation.

The Prone position is a patient position used during surgical procedures that provide surgical access to the dorsal aspects of the patient’s body.
PRONE POSITION DEFINITION SERIES
AMSCO 400 Series Small Steam Sterilizer.
Surgical Instrument Cleaning Chemistries.Sterile Processing Department Accessories.Surgical and Medical Examination Lights.
PRONE POSITION DEFINITION PROFESSIONAL


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
